“National Center ICSC – “National Center for HPC, Big Data and Quantum Computing – Cascade Call Spoke 9 – “Digital Society & Smart City” – CUP E63C22000980007 IDENTIFICATION CODE CN_00000013
High-performance computing for Weather nowcasting with Federated Artificial Intelligence
A demonstrator based on an HPC framework for weather forecasting
The project “High-performance computing for Weather nowcasting with Federated Artificial Intelligence” (Hi-WeFAI) aims to develop and implement a demonstrator in an operational environment based on an HPC framework for weather forecasting. The demonstrator will use a system based on Federated Learning and Artificial Intelligence (FAI) and a network of meteorological sensors of different natures (X-Band Weather Radar, Weather Stations).
Improve the accuracy of short-term weather forecasts
Hi-WeFAI aims to improve the accuracy of short-term weather forecasts to produce warning messages, filling the gap due to the limitations imposed by the classical computational approach.
The partnership chose the metropolitan area of Naples as the study area, leveraging its previous experience.

The motivations that led to the project idea are sought in light of climate change as essential to pay attention to intense meteorological events that can generate floods, whose impact on the socio-economic fabric is strengthened by the growing anthropic pressure.
Overcome the limitations of the classical numerical approach to detect sub-grid phenomena
The development of numerical weather forecasting techniques, the improvement of the characterization of the state of the atmosphere, and the increase in the computational power of high-performance computing systems have allowed the production of accurate medium-term forecasts. However, intense meteorological events are often less extensive phenomena than the resolution of the computational domains used by numerical meteorological models. As it is difficult to predict, the proposed solution has the ambition to overcome the limitations of the classical numerical approach to detect sub-grid phenomena.
Using FAI in this context offers new opportunities to create integrated forecasting/predictive models that will allow decision-makers to mitigate the impact of intense meteorological phenomena and protect local communities.
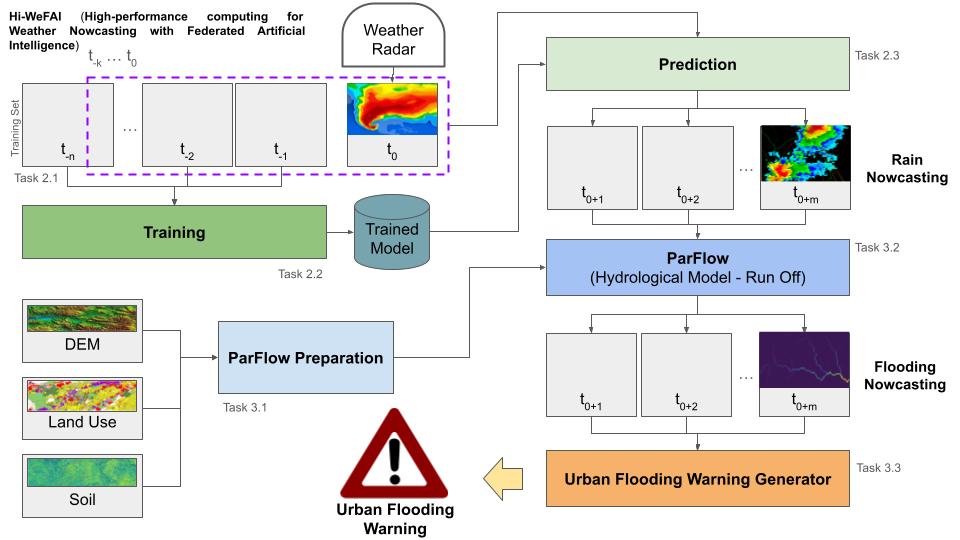
The acquired data will train a prediction model for short-term precipitation. In the inference phase, this will allow the creation of the input dataset for a hydrometeorological model. The project will use the results of this model to generate flood warning messages in urban areas.
Global collaboration to tackle climate change

University of Naples “Parthenope”
Leading research organization
- Raffaele Montella
- Giorgio Budillon
- Angelo Ciaramella
- Yuri Cotroneo
- Antonio Maratea
- Livia Marcellino
- Mariacarla Staffa

Fides consulting
Industrial partner
- Irene Violini
- Davide Battipaglia
- Fata Campochiaro
- Carlo De Simone

Work packages
WP.1: Project Management
WP1 aims to ensure the execution of the work plan, quality control, knowledge management, and effective communication between stakeholders. This work package also includes procurement activities for the necessary infrastructure (hardware/software). Furthermore, WP1 manages the project as a whole, including reporting activities, supervision of data management, and financial, legal, administrative, and technical matters. It also includes technical coordination of activities between the various WPs of the project, regular communication between project members (video conferences, meetings), monitoring of project performance, risk analysis, and contingency management, as well as planning, monitoring, and justification of resource allocation.
WP.2: Analysis
WP2 concerns analyzing the requirements to be carried out after collecting specifications to define Hi-WeFAI.
Nowcasting consists of predicting meteorological behaviors with an advance of a few minutes to hours, allowing local authorities to be warned of dangerous situations. Nowcasting is based on data detected by weather radars, which allow meteorologists to produce highly detailed forecasts specific to the location. Adaptable solutions for federated learning models for XWR and WS and the generative model for synthesizing the dataset to be used with input for the hydrometeorological model are analyzed in this WP.
WP.3: Design
WP3 aims to design and develop a nowcasting model based on AI techniques for XWR and WS instruments. In this phase, the design of the software infrastructure to implement the FAI, the individual models on the edge computing resources for XWR and WS, the generative model for the synthesis of the dataset to be used with the hydrometeorological model, the decisional component for the activation of said model, and the system for the dissemination of the results are carried out.
WP.4: Implementation
A large sample of reflectivity data collected between 2018 and 2023 will be pre-processed to train the nowcasting model by suitably simulating the federated learning through the two different XWRs available. Once the federated learning procedure has been implemented and the ad-hoc protocol based on the DTF has been developed, the generative model for the synthesis of the precipitation prediction dataset as input for the hydrometeorological model is implemented and the decisional component for the activation of the hydrometeorological model is implemented. In this WP all the static data necessary for the configuration of the hydrometeorological model are prepared. The ParFlow implementation of the Hi-WeFAI project will be validated in WP5.
The DAGOnStar workflow engine will be used and extended with a new software component for generating automatic alerts provided by the direct interface with different notification technologies.
WP.5: Use Case
WP5 is dedicated to hydrometeorological nowcasting, evaluating each component of the workflow. The predictions of the precipitation field evolution provided by the deep learning model in the next 180 minutes will be compared with the precipitation data observed on the ground (XWR, WS) using different statistical indices.
WP.6: Cloud Infrastructure for Federated Learning
Within WP6, the use case will be tested on on-premises, cloud, and hybrid computing resources thanks to the experience of industrial partners.
WP.7: Dissemination
WeFAI releases, and the public dissemination of the project. A dedicated web portal for the project will be created. Workshops and technical presentations will be held to foster knowledge exchange with other research groups, companies, and associations, as well as training events, discussion forums, and mailing lists. Promotional material will be prepared to present the project results and encourage their use.
DNSH Principles: The project is consistent with the specific principles and obligations of the PNRR relating to the “Do No Significant Harm” (DNSH) principle since it has no significant impact on the environment. The use case allows the 6 objectives of EU regulation 2020/852 to be considered, partially or entirely, as beneficiaries of the project results.
Contacts
Project referent: Prof. Raffaele Montella
Department of Science and Technologies (DiST), University of Naples “Parthenope”, Centro Direzionale ISOLA C4, 80133 Napoli NA
+39 0815476672 | +39 3393055922
info@hiwefai-project.org | raffaele.montella@uniparthenope.it

